Jodi Cooley named fellow of American Association for the Advancement of Science
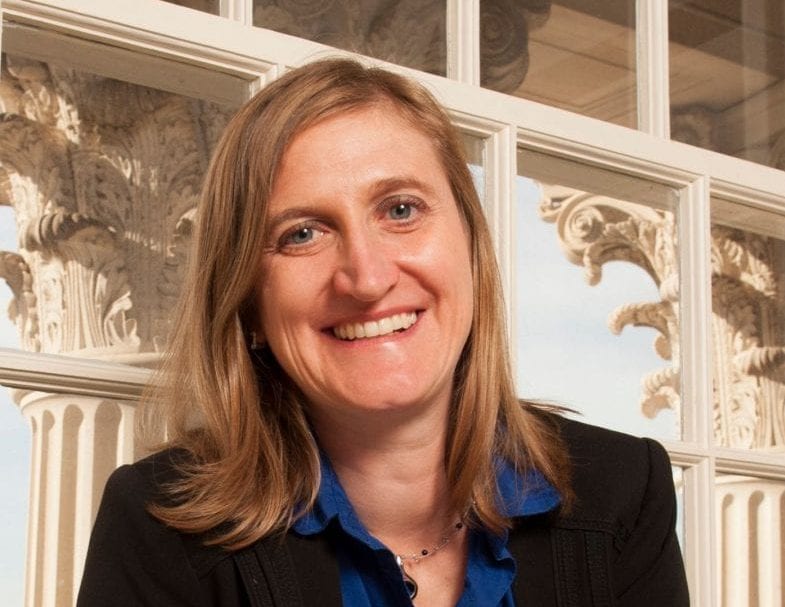
DALLAS (SMU) – SMU physicist Jodi Cooley has been named a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). Election as an AAAS Fellow is an honor bestowed by their peers upon the group’s members for scientifically or socially distinguished efforts to advance science or its applications.
Cooley is one of 416 fellows to be honored during the 2019 AAAS annual meeting in Washington, D.C., on Saturday, Feb. 16. She is being honored for her contributions to the search for dark matter scattering with nuclei, particularly using cryogenic technologies. The nature of dark matter is unknown, but is believed to make up about 85 percent of the universe.
“I feel incredibly privileged to have even been nominated for such an honor; to be further elected as a Fellow of the AAAS is humbling beyond words,” Cooley said. “I also feel an immense sense of gratitude toward all of those who supported me along this path: my family, my friends, and my mentors.”
Cooley, who joined SMU in 2009, is associate professor of experimental particle physics in SMU’s Dedman College of Humanities and Sciences.
“Professor Cooley is a distinguished scientist with a record of outstanding federal research support and innovative experimental design,” said Dedman College Dean Thomas DiPiero. “In addition to her work in the lab and in the classroom, she also reaches out to the general public to explain the intricacies of particle physics in ways that are understandable and engaging.”
Cooley and her colleagues operated sophisticated detectors in the Soudan Underground Laboratory, MN. The Department of Energy and National Science Foundation announced they’ll provide funding to expand that research, so planning is now under way to move the experiment to an even deeper location, SNOLAB in Canada, to improve the search for dark matter. These detectors can distinguish between elusive dark matter particles and background particles that mimic dark matter interactions.
Cooley is a principal investigator on the SuperCDMS dark matter experiment and was principal investigator for the AARM collaboration, whose aim was to develop integrative tools for underground science. She has won numerous awards for her research, including an Early Career Award from the National Science Foundation and the Ralph E. Powe Junior Faculty Enhancement Award from the Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
Cooley received a B.S. degree in applied mathematics and physics from the University of Wisconsin in Milwaukee in 1997. She earned her master’s degree in 2000 and her Ph.D. in 2003 at the University of Wisconsin – Madison for her research searching for neutrinos from diffuse astronomical sources with the AMANDA-II detector. Upon graduation she did postdoctoral studies at both MIT and Stanford University.
The tradition of AAAS Fellows began in 1874. Currently, members can be considered for the rank of Fellow if nominated by the steering groups of the Association’s 24 sections, or by any three Fellows who are current AAAS members (so long as two of the three sponsors are not affiliated with the nominee’s institution), or by the AAAS chief executive officer. Fellows must have been continuous members of AAAS for four years by the end of the calendar year in which they are elected. AAAS Fellow’s lifetime honor comes with an expectation that recipients maintain the highest standards of professional ethics and scientific integrity.
Each steering group reviews the nominations of individuals within its respective section and a final list is forwarded to the AAAS Council, which votes on the aggregate list. The Council is the policymaking body of the Association, chaired by the AAAS president, and consisting of the members of the board of directors, the retiring section chairs, delegates from each electorate and each regional division, and two delegates from the National Association of Academies of Science.
About SMU
SMU is the nationally ranked global research university in the dynamic city of Dallas. SMU’s alumni, faculty and nearly 12,000 students demonstrate an entrepreneurial spirit as they lead change in their professions, communities and the world.
About the AAAS
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the journal Science (www.sciencemag.org) as well as Science Translational Medicine, Science Signaling, a digital, open-access journal, Science Advances, Science Immunology, and Science Robotics. AAAS was founded in 1848 and includes nearly 250 affiliated societies and academies of science, serving 10 million individuals. Science has the largest paid circulation of any peer-reviewed general science journal in the world. The non-profit AAAS (www.aaas.org) is open to all and fulfills its mission to “advance science and serve society” through initiatives in science policy, international programs, science education, public engagement, and more. For the latest research news, log onto EurekAlert! (www.eurekalert.org), the premier science-news Web site, a service of AAAS. See www.aaas.org.