By: TAI Professor Mark Allen
 As someone who has studied both art and philosophy, people regularly ask me what, if anything, they have in common. While I think that there are many fascinating ways in which these two domains overlap, one similarity that I find particularly interesting is the intersection of ethics and aesthetics.
As someone who has studied both art and philosophy, people regularly ask me what, if anything, they have in common. While I think that there are many fascinating ways in which these two domains overlap, one similarity that I find particularly interesting is the intersection of ethics and aesthetics.
One way that ethics and aesthetics are similar is that they both deal with value. When we say that a painting or a deed is “good,” at least one of the things we mean is that the thing or action in question has value. When we say that a painting or a deed is “bad,” at least one of the things we mean is that it has little value, or even negative value insomuch that it diminishes our experience of life or the world around us. It’s why we use words like “beautiful” and “ugly” interchangeably to describe both artistic works and moral acts.
– That was a beautiful song.
– That was a beautiful thing you did.
– That sculpture is ugly.
– That was a really ugly thing to say.
In other words, murder is not merely wrong, there is something truly ugly about it. And when a painter puts the final brushstroke on the canvas, there is something distinctly right about it. So, there seems to be an aesthetic dimension to the moral life and an ethical dimension to the aesthetic.
Whether it be moral or artistic, things of value improve our lives in some way. But it is important to point out that many of the things we value most (like good art and good deeds) are worth pursuing for their own sake, regardless of any utilitarian benefit we get out of them. Sure, listening to certain types of music can lower blood pressure and reduce anxiety. Those who live a life of kindness and generosity often experience the rush of positive feelings and a general sense of well-being. Such benefits are real and welcome, but nonetheless secondary. Good music is valuable even if it doesn’t reduce our heart rate (sometimes it does just the opposite). Acts of kindness and generosity often go unnoticed and lead to self-sacrifice.
Another thing that the spheres of ethics and aesthetics share is the concept of wisdom. No one appreciates it when their difficult seasons or ethical dilemmas are met with oversimplified advice and platitudes from those who mean well, but lack the awareness and nuanced sensitivity that a situation calls for. so often life doesn’t seem to play by any rules, which is why—when things gets complicated—we seek out the counsel of the wise, not just the intelligent or talented. Nor those who have simply memorized a rigid code of conduct: Always do this. Never do that.
Of course, it’s important to start with the “unbreakable” rules that all people everywhere value: don’t murder, don’t steal, don’t lie. We instruct children to tell the truth, to be kind and to respect their elders. And yet, as they mature we explain that there may come a time when other rules come into play. When a stranger asks if a parent is home; when a bully is cruel to the weak or marginalized; when an adult behaves inappropriately toward a child. It such cases, it’s not time to be nice. But the proper responses in these situations are not somehow violations of the fundamental moral principles of truth, kindness and respect—quite the contrary, the fitting responses are based on and upheld by the most basic fundamentals.
Over the course of my career I’ve been able to witness these parallels play out in the classroom, particularly my design classes. [1] Pick up any good textbook on the topic and more than likely you’ll find a set of rules that, when followed, lead to good design. My go-to text for beginners is Timothy Samara’s Design Elements, which starts off with just such a section entitled, “Twenty Rules You Should Never Break.” Here Samara makes it clear that students of design should:
#4 Never use more than two typefaces.
#8 Never fill up all the negative space in a layout.
#18 Always make sure your composition is dynamic and full of motion.” [2]
I like Samara because he is great for beginners in that he gives clear-cut, easy-to-follow rules that help students avoid some of the most common pitfalls that the untrained or self-taught designer may struggle with. However, the complaint I frequently get after a few weeks is that Samara’s method is a very strict and narrow way to approach such an artful discipline. I mean, is the process of design really just a set of rules? A flowchart of do’s and don’ts?
In one sense, I think my students are right to complain—the book does start off in a rather rigid fashion. Always do this, never do that. But the other big reason I use this text is the way Samara ends the book with a chapter devoted to examples of how each and every one of his twenty rules can be broken. Of course, Samara saves this chapter for the end because he is a seasoned professional and an experienced educator. He knows that, until students master the fundamentals, they have not yet developed the aesthetic savvy needed to flex foundational principles like an experienced pro. The fact that Samara offers up twenty ways to break his twenty rules is not proof that aesthetic relativism is true; it only reveals that both skill and experience are needed in order to become a good designer.
When teaching through this text I always stress that Samara does not end his book by saying “Now, throw out all the rules I mentioned earlier and do whatever you want because, after all, beauty is in the eye of the beholder.” If this were true we could choose type, color and style arbitrarily, despite the context or meaning of the work. By contrast, Samara provides detailed, illustrated examples of legitimate exceptions—not contradictions. It’s why the actual name of his final chapter is “When and Why to Break Every Rule in this Book.”
Personally, I wish Samara had used a different word than “break” because it’s not as if he is teaching students to actually violate or contradict any fundamental rules of design here. He’s making an appeal to a higher (yet complementary) set of principles that can only be properly wielded with a great deal of knowledge and experience. The examples he gives are exceptions based on more advanced rules that don’t translate well into pithy lists, templates or 140 characters—methods that are the domain of master designers and artists. Perhaps there is a proper time and place for truisms and templates, but with complex themes and problems comes the need for artists who have more than just a set of skills, but in a very real sense demonstrate a certain kind of artistic wisdom.
Aristotle’s approach to ethics most closely embodies what I’m trying to demonstrate and is largely based on what is known as the Golden Mean—that is, finding a “middle” way between the extremes of deficiency and excess. For example, courage is a virtue with respect to how someone responds to danger—if taken to one extreme in excess, it becomes recklessness, while the deficient extreme manifests itself as cowardice. It is no accident that Aristotle uses art as a way to illustrate this concept in his Nicomachean Ethics:
“Hence people are accustomed to saying that there is nothing to take away from or add to works [of art] that are in a good state, on the grounds that the good state is destroyed by excess and deficiency but the mean preserves it; and the good craftsmen, as we say, perform their work by looking to this.” [3]
Aristotle says that we should always strive to be courageous (which might sound dogmatic). But he also says it’s important to take the particular person and situation into consideration (which might sound relativistic). But the beauty of his system is that the mean is not the exact middle, nor is it always found in the same place along the continuum between excess and deficiency. [4] Some situations call for the courageous person to act in a way that is closer to the reckless end of the spectrum, while in other situations what is courageous may seem like cowardice. For instance, a 6’4” military officer who wrestles an armed terrorist to the ground in order to save a train full of people vs. Rosa Parks who simply refused to give up her seat on a bus. Both people did the right thing—the equally courageous thing—but they did so in a way that was fitting for each context. [5]
In summary, when it comes to ethics, the well-lived life certainly comes with its fair share of rules—but it is the wise among us who are most skilled at navigating life’s complex seasons and dilemmas with earned experience and a familiarity with those moral principles of a higher but complementary order. Likewise, the fundamentals of art and design are inescapably important—in fact they form the only foundation from which more advanced skills and principles can be applied or even thought. The fact that such striking parallels show up across the seemingly unrelated disciplines of art and philosophy reveals something significant about the world and our shared experience of it—namely, that values like truth, goodness and beauty are perhaps aspects of reality itself and represent common goals toward which all humanity strives (whether we are conscious of it or not).
NOTES:
[1] While I will focus here on parallels between philosophy and design, it should be noted that legendary advertising icon, Bill Bernbach, studied philosophy at NYU and remained an avid reader of philosophical works throughout his life. In fact, in a speech speech he gave to the 4A’s (the American Association of Advertising Agencies) in 1980, he specifically mentions Aristotle, St. Augustine and Bertrand Russell (among other thinkers) and relates their work to the task of advertising.
[2] Samara, Design Principles, pp. 10-23.
[3] Aristotle, Nicomachean Ethics, 1106b 10-14.
[4] It is important to note here that the “middle” state that Aristotle advocates is not the exact middle or “average” between extremes, but rather a mean relative to the situation. With this feature, Aristotle’s ethics avoid the moderation fallacy (Ex: Jim isn’t paying attention and backs into Pam’s car. Even though it’s Jim’s fault, he offers to do what’s “fair” by meeting her in the middle and paying for half of the damages).
[5] Aristotle also points out that certain vices that are not on a continuum between extremes, so there is no mean. Ex: there is no “just right” amount of racism, cruelty or adultery.
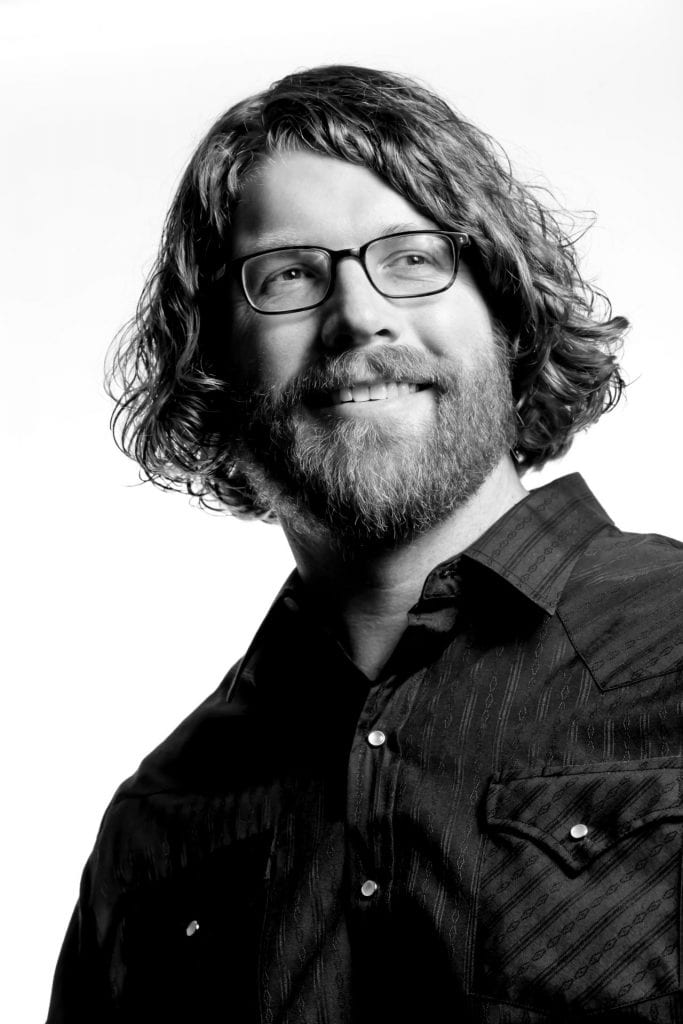
 Throughout his career, Temerlin professor Dr. Mark Allen has worked as an art director and designer for clients including the History Channel, the New York Yankees, Norton/Symantec, Martha Stewart, The Walking Dead, A&E Networks, HBO, the U.S. National Parks Service and the Vietnam Veterans Memorial Fund. His work has been recognized for creative excellence in the Print Regional Design Annual and Applied Arts magazine and by the Promotion Marketing Association, the Illustrators Society of Los Angeles and the Dallas Society of Visual Communications. He joined SMU’s newly established Temerlin Advertising Institute in 2003, where he currently teaches various creative advertising courses. Allen recently shared his insights into his students’ work and the shift in teaching creative courses brought about by the pandemic.
Throughout his career, Temerlin professor Dr. Mark Allen has worked as an art director and designer for clients including the History Channel, the New York Yankees, Norton/Symantec, Martha Stewart, The Walking Dead, A&E Networks, HBO, the U.S. National Parks Service and the Vietnam Veterans Memorial Fund. His work has been recognized for creative excellence in the Print Regional Design Annual and Applied Arts magazine and by the Promotion Marketing Association, the Illustrators Society of Los Angeles and the Dallas Society of Visual Communications. He joined SMU’s newly established Temerlin Advertising Institute in 2003, where he currently teaches various creative advertising courses. Allen recently shared his insights into his students’ work and the shift in teaching creative courses brought about by the pandemic.