From picking apart atomic particles at Switzerland’s CERN, to unraveling the mysterious past, to delving into the human psyche, SMU researchers are in the vanguard of those helping civilization understand more and live better.
With both public and private funding — and the assistance of their students — they are tackling such scientific and social problems as brain diseases, immigration, diabetes, evolution, volcanoes, panic disorders, childhood obesity, cancer, radiation, nuclear test monitoring, dark matter, the effects of drilling in the Barnett Shale, and the architecture of the universe.
The sun never sets on SMU research
Besides working in campus labs and within the Dallas-area community, SMU scientists conduct research throughout the world, including at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider, and in Angola, the Canary Islands, Mongolia, Kenya, Italy, China, the Congo Basin, Ethiopia, Mexico, the Northern Mariana Islands and South Korea.
“Research at SMU is exciting and expanding,” says Associate Vice President for Research and Dean of Graduate Studies James E. Quick, a professor in the Huffington Department of Earth Sciences. “Our projects cover a wide range of problems in basic and applied research, from the search for the Higgs particle at the Large Hadron Collider in CERN to the search for new approaches to treat serious diseases. The University looks forward to creating increasing opportunities for undergraduates to become involved as research expands at SMU.”
Funding from public and private sources
In 2009-10, SMU received $25.6 million in external funding for research, up from $16.5 million the previous year.
“Research is a business that cannot be grown without investment,” Quick says. “Funding that builds the research enterprise is an investment that will go on giving by enabling the University to attract more federal grants in future years.”
The funding came from public and private sources, including the National Science Foundation; the National Institutes of Health; the U.S. Departments of Agriculture, Defense, Education and Energy; the U.S. Geological Survey; Google.org; the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation; Texas’ own Hogg Foundation for Mental Health; and the Texas Instruments Foundation.
Worldwide, the news media are covering SMU research. See some of the coverage. Browse a sample of the research:
CERN and the origin of our universe
 Led by Physics Professor Ryszard Stroynowski, SMU physics researchers belong to the global consortium of scientists investigating the origins of our universe by monitoring high-speed sub-atomic particle collisions at CERN, the world’s largest physics experiment.
Led by Physics Professor Ryszard Stroynowski, SMU physics researchers belong to the global consortium of scientists investigating the origins of our universe by monitoring high-speed sub-atomic particle collisions at CERN, the world’s largest physics experiment.
Compounds to fight neurodegenerative diseases

Synthetic organic chemist and Chemistry Professor Edward Biehl leads a team developing organic compounds for possible treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s, Huntington’s and Alzheimer’s. Preliminary investigation of one compound found it was extremely potent as a strong, nontoxic neuroprotector in mice.
Hunting dark matter
 Assistant Professor of Physics Jodi Cooley belongs to a high-profile international team of experimental particle physicists searching for elusive dark matter — believed to constitute the bulk of the matter in the universe — at an abandoned underground mine in Minnesota, and soon at an even deeper mine in Canada.
Assistant Professor of Physics Jodi Cooley belongs to a high-profile international team of experimental particle physicists searching for elusive dark matter — believed to constitute the bulk of the matter in the universe — at an abandoned underground mine in Minnesota, and soon at an even deeper mine in Canada.
Robotic arms for injured war vets

Electrical Engineering Chairman and Professor Marc Christensen is director of a new $5.6 million center funded by the Department of Defense and industry. The center will develop for war veteran amputees a high-tech robotic arm with fiber-optic connectivity to the brain capable of “feeling” sensations.
Green energy from the Earth’s inner heat

The SMU Geothermal Laboratory, under Earth Sciences Professor David Blackwell, has identified and mapped U.S. geothermal resources capable of supplying a green source of commercial power generation, including resources that were much larger than expected under coal-rich West Virginia.
Exercise can be magic drug for depression and anxiety

Psychologist Jasper Smits, director of the Anxiety Research and Treatment Program at SMU, says exercise can help many people with depression and anxiety disorders and should be more widely prescribed by mental health care providers.
The traditional treatments of cognitive behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy don’t reach everyone who needs them, says Smits, an associate professor of psychology.
Virtual reality “dates” to prevent victimization
![]()
SMU psychologists Ernest Jouriles, Renee McDonald and Lorelei Simpson have partnered with SMU Guildhall in developing an interactive video gaming environment where women on virtual-reality dates can learn and practice assertiveness skills to prevent sexual victimization.
With assertive resistance training, young women have reduced how often they are sexually victimized, the psychologists say.
Controlled drug delivery agents for diabetes
 Associate Chemistry Professor Brent Sumerlin leads a team of SMU chemistry researchers — including postdoctoral, graduate and undergraduate students — who fuse the fields of polymer, organic and biochemistries to develop novel materials with composite properties. Their research includes developing nano-scale polymer particles to deliver insulin to diabetics.
Associate Chemistry Professor Brent Sumerlin leads a team of SMU chemistry researchers — including postdoctoral, graduate and undergraduate students — who fuse the fields of polymer, organic and biochemistries to develop novel materials with composite properties. Their research includes developing nano-scale polymer particles to deliver insulin to diabetics.
Sumerlin, associate professor of chemistry, was named a 2010-2012 Alfred P. Sloan Research Fellow, which carries a $50,000 national award to support his research.
Human speed
 An expert on the locomotion of humans and other terrestrial animals, Associate Professor of Applied Physiology and Biomechanics Peter Weyand has analyzed the biomechanics of world-class athletes Usain Bolt and Oscar Pistorius. His research targets the relationships between muscle function, metabolic energy expenditure, whole body mechanics and performance.
An expert on the locomotion of humans and other terrestrial animals, Associate Professor of Applied Physiology and Biomechanics Peter Weyand has analyzed the biomechanics of world-class athletes Usain Bolt and Oscar Pistorius. His research targets the relationships between muscle function, metabolic energy expenditure, whole body mechanics and performance.
Weyand’s research also looks at why smaller people tire faster. Finding that they have to take more steps to cover the same distance or travel at the same speed, he and other scientists derived an equation that can be used to calculate the energetic cost of walking.
Pacific Ring of Fire volcano monitoring
 An SMU team of earth scientists led by Professor and Research Dean James Quick works with the U.S. Geological Survey to monitor volcanoes in the Pacific Ocean’s Ring of Fire near Guam on the Northern Mariana Islands. Their research will help predict and anticipate hazards to the islands, the U.S. military and commercial jets.
An SMU team of earth scientists led by Professor and Research Dean James Quick works with the U.S. Geological Survey to monitor volcanoes in the Pacific Ocean’s Ring of Fire near Guam on the Northern Mariana Islands. Their research will help predict and anticipate hazards to the islands, the U.S. military and commercial jets.
The two-year, $250,000 project will use infrasound — in addition to more conventional seismic monitoring — to “listen” for signs a volcano is about to blow.
Reducing anxiety and asthma
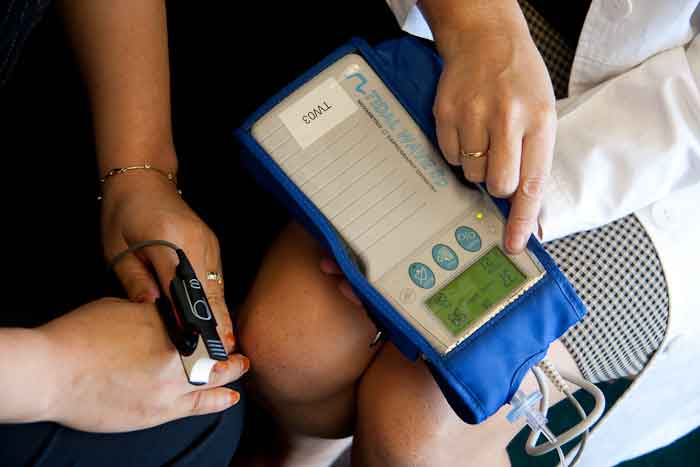 A system of monitoring breathing to reduce CO2 intake is proving useful for reducing the pain of chronic asthma and panic disorder in separate studies by Associate Psychology Professor Thomas Ritz and Assistant Psychology Professor Alicia Meuret.
A system of monitoring breathing to reduce CO2 intake is proving useful for reducing the pain of chronic asthma and panic disorder in separate studies by Associate Psychology Professor Thomas Ritz and Assistant Psychology Professor Alicia Meuret.
The two have developed the four-week program to teach asthmatics and those with panic disorder how to better control their condition by changing the way they breathe.
Breast Cancer community engagement
 Assistant Psychology Professor Georita Friersen is working with African-American and Hispanic women in Dallas to address the quality-of-life issues they face surrounding health care, particularly during diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.
Assistant Psychology Professor Georita Friersen is working with African-American and Hispanic women in Dallas to address the quality-of-life issues they face surrounding health care, particularly during diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer.
Friersen also examines health disparities regarding prevention and treatment of chronic diseases among medically underserved women and men.
Paleoclimate in humans’ first environment
 Paleobotanist and Associate Earth Sciences Professor Bonnie Jacobs researches ancient Africa’s vegetation to better understand the environmental and ecological context in which our ancient human ancestors and other mammals evolved.
Paleobotanist and Associate Earth Sciences Professor Bonnie Jacobs researches ancient Africa’s vegetation to better understand the environmental and ecological context in which our ancient human ancestors and other mammals evolved.
Jacobs is part of an international team of researchers who combine independent lines of evidence from various fossil and geochemical sources to reconstruct the prehistoric climate, landscape and ecosystems of Ethiopia in particular. She also identifies and prepares flora fossil discoveries for Ethiopia’s national museum.
Ice Age humans

Anthropology Professor David Meltzer explores the western Rockies of Colorado to understand the prehistoric Folsom hunters who adapted to high-elevation environments during the Ice Age.
Meltzer, a world-recognized expert on paleoIndians and early human migration from eastern continents to North America, was inducted into the National Academy of Scientists in 2009.
Understanding evolution
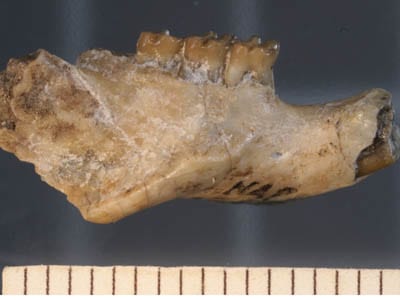 The research of paleontologist Alisa WInkler focuses on the systematics, paleobiogeography and paleoecology of fossil mammals, in particular rodents and rabbits.
The research of paleontologist Alisa WInkler focuses on the systematics, paleobiogeography and paleoecology of fossil mammals, in particular rodents and rabbits.
Her study of prehistoric rodents in East Africa and Texas, such as the portion of jaw fossil pictured, is helping shed more light on human evolution.















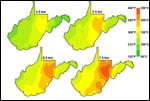

 The U.S. Department of Energy’s Rocky Mountain Oilfield Testing Center, RMOTC, in partnership with the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory, NREL, and Southern Methodist University
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Rocky Mountain Oilfield Testing Center, RMOTC, in partnership with the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory, NREL, and Southern Methodist University