Wired reporter Emily Reynolds covered the research of SMU planetary scientist and research assistant professor Matthew Siegler and a team of scientists who discovered the moon wandered off its axis billions of years ago due to a shift in its mass most likely caused by volcanic activity.
The article, “The Moon used to spin on a different axis,” published March 24. A report on the discovery of the rare event was published today in Nature: that Earth’s moon slowly moved from its original axis roughly 3 billion years ago.
EXCERPT:
By Emily Reynolds
Wired
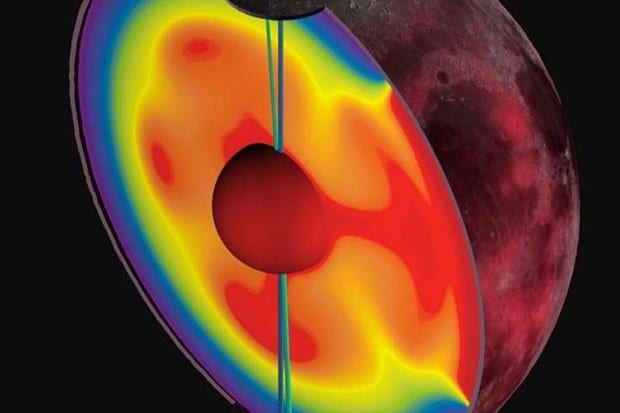
The Moon used to “spin on a different axis” that was subject to “polar wander,” a new study into the satellite’s early history has said.The Planetary Science Institute study, published in Nature, highlights two regions full of hydrogen deposits near the Moon’s two poles. This, it says, suggests the presence of ice — ice that only would have survived if it had remained in permanent shadow.
“If the orientation of the Moon has changed, then the locations of the shadowed regions will also have changed,” the researchers write.
The poles “wandered”, according to the team, because of volcanic activity in the area, which would have warmed. It also would have made them less dense, causing the “wandering” of the axes.
“The Moon has a single region of the crust where radioactive elements ended up as the Moon was forming,” said Matthew Siegler, lead author of the study. “This radioactive crust acted like an oven broiler heating the mantle below.”
“This giant blob of hot mantle was lighter than cold mantle elsewhere, causing the whole Moon to move.”
The shift probably happened over three billion years ago, the team say, and would have meant the Moon showed a completely different face. Overall, the Moon shifted around six degrees over one billion years. Only a few other planetary bodies have been said to shift their axes — Earth and Mars, as well as two moons of Saturn and Jupiter.
“The same face of the Moon has not always pointed towards Earth,” said Siegler. “As the axis moved, so did the face of the Man in the Moon. He sort of turned his nose up at the Earth.”
Follow SMUResearch.com on twitter at @smuresearch.
SMU is a nationally ranked private university in Dallas founded 100 years ago. Today, SMU enrolls nearly 11,000 students who benefit from the academic opportunities and international reach of seven degree-granting schools. For more information see www.smu.edu.
SMU has an uplink facility located on campus for live TV, radio, or online interviews. To speak with an SMU expert or book an SMU guest in the studio, call SMU News & Communications at 214-768-7650.


 NASA data leads to rare discovery: Earth’s moon wandered off axis billions of years ago
NASA data leads to rare discovery: Earth’s moon wandered off axis billions of years ago Good news! You’re likely burning more calories than you thought
Good news! You’re likely burning more calories than you thought New look at Pizarro’s conquest of Inca reveals foot soldiers were awed by empire’s grandeur
New look at Pizarro’s conquest of Inca reveals foot soldiers were awed by empire’s grandeur